Spreader
The Spreader component allows users to create custom synthetic spreads across different products at one exchange, or across multiple exchanges. Users may determine the parameters of their synthetic spread and place orders in the generated synthetic market, allowing Spreader to work individual legs to achieve the user’s desired strategy.
Spreader Configuration
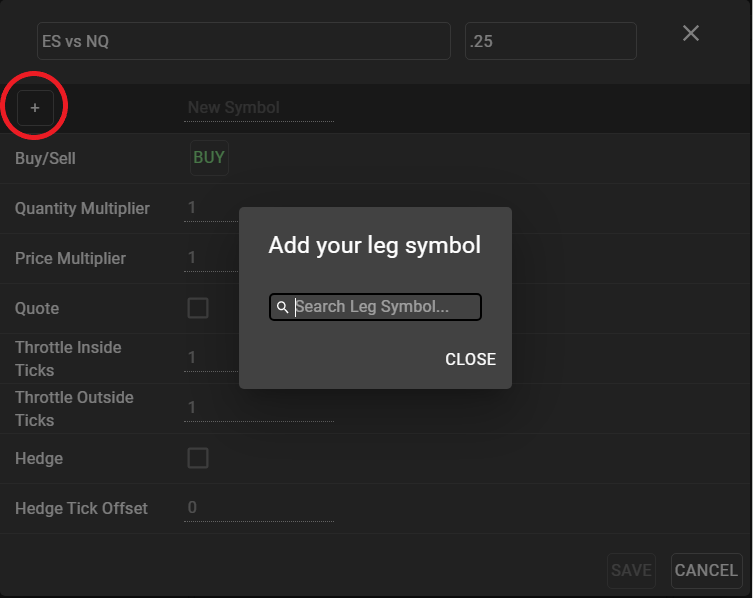
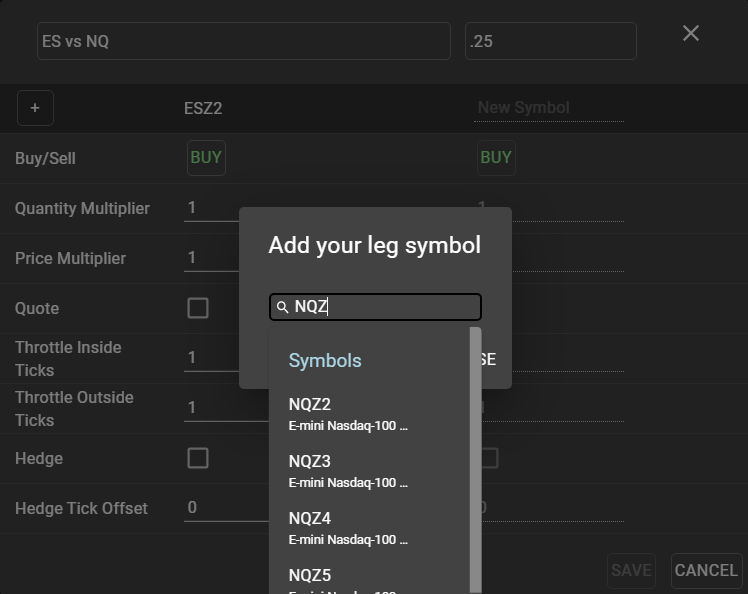
To create a synthetic spread instrument, select ‘New’ from the Spreader component window to open a spread configuration template. Use the ‘+’ sign in the Spreader configuration window to add individual legs. Contracts may be found using the same search techniques as in Main Search, detailed here.
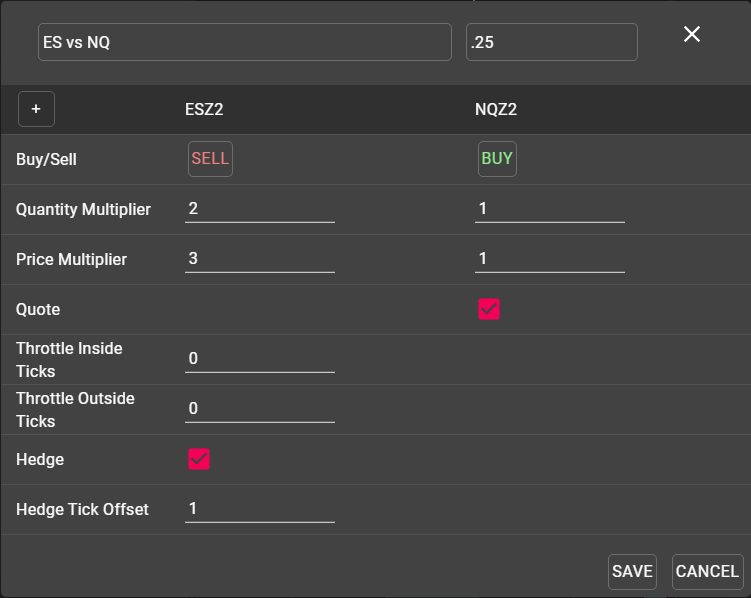
Spread Name: Each synthetic spread must be named. This name can be edited at any time, and users may create as many different spreads as desired, but each spread name must be unique.
Tick Size: Used to determine the price increment in which the spread will be displayed once the synthetic market is generated.
Buy/Sell: Choose the direction of the legs of the spread. There is no restriction on the number of legs a spread may contain, nor on the direction of the legs.
Quantity Multiplier: Determines the ratio in which the spread will trade. In the above example, this spread will work to execute 2 ES contracts for every 1 NQ contract.
Price Multiplier: Determines the ratio of the displayed price of the spread. Adjusting the Price Multiplier will not affect the manner in which the spread is executed. Rather, the Price Multiplier, in conjunction with Tick Size, allows users to manipulate the display of the synthetic spread within their workspace. In the above example, the Price multiplier of 3:1 is intended to provide a displayed spread price close to even money, without the need to execute the legs in that ratio.
Quote: Determines which leg of the spread will be used as the quote leg, or lead leg. At least one leg of all spreads must be designated as the quote leg.
Hedge: Determines which leg(s) of the spread will be hedged in order to achieve the desired price, once a quote leg has been executed.
Throttle Ticks: These two settings are used to determine how often the spread will be re-priced in the market. These settings are most often used to restrict the amount of messaging sent to the exchange. A lower value in these fields will allow the spread to re-price more frequently, while a higher value will serve to restrict the spread from requoting as often. A value of zero in each field will allow the spread to re-price with every tick in the market, as is the case in the above example.
Outside Ticks will specify how many ticks the spread must move away from the user’s desired price before re-quoting, while Inside Ticks specifies the number of ticks the spread price must move towards the user’s desired price before re-quoting.
Hedge Tick Offset: Sometimes referred to as payup ticks, this setting specifies how many ticks the user is willing to sacrifice when firing the hedge leg of the spread. A value of zero will result in the hedge leg firing only at the price required to meet the desired spread price, but may result in fewer executions on the hedge leg and more hangs. A higher value in this field allows for slippage in the executed spread price and is most often used to achieve a full fill on the spread quantity, with less concern for the final price of the synthetic spread.
In the above example, with Hedge Tick Offset set to 1, the hedge order will be submitted one tick worse than the level needed to achieve the desired spread price to reduce the chances of getting hung.
Viewing Synthetic Spreads and Placing Spreader Orders
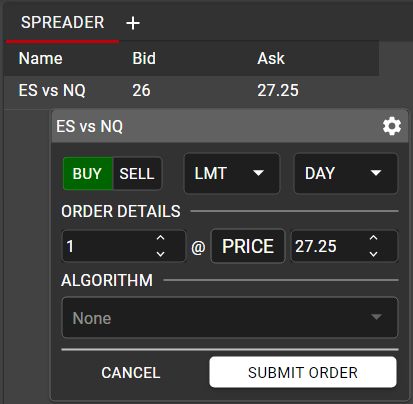
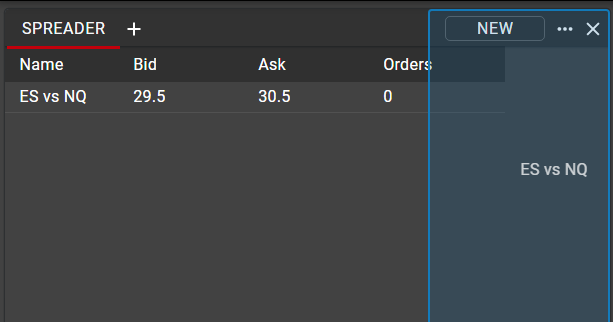
Once a synthetic spread has been created, named and saved, the spread will be shown in Spreader window as a single instrument, with the top of the synthetic market Bid and Ask displayed.
Orders may be entered directly from the Spreader window in the same manner as they are in Hot Watch. A single left click on the Bid will open a floating Order Ticket, pre-populated as a Sell, while a single left click on the Ask will open a floating Order Ticket pre-populated as a Buy. All fields may be manipulated in the Order Ticket before the order is sent.
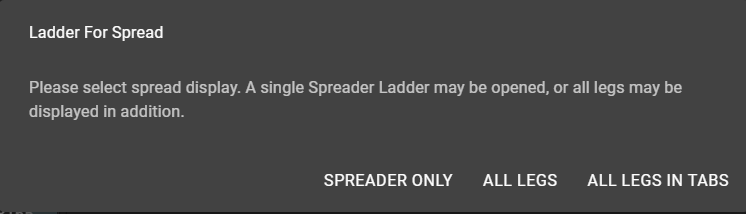
Most users will want to see their synthetic spreads displayed in a Ladder. This can be accomplished by dragging and dropping the spread name from the Spreader window. Dragging into a space on the canvas will generate a new Ladder for the synthetic instrument, or the spread may be added to an existing Ladder component as a new tab.
When adding a new Ladder for a Spreader instrument, users have the choice to display only the synthetic instrument, or to display each component leg of the Spreader in separate Ladders or tabs. When adding a new Ladder, users will be presented with the following display:
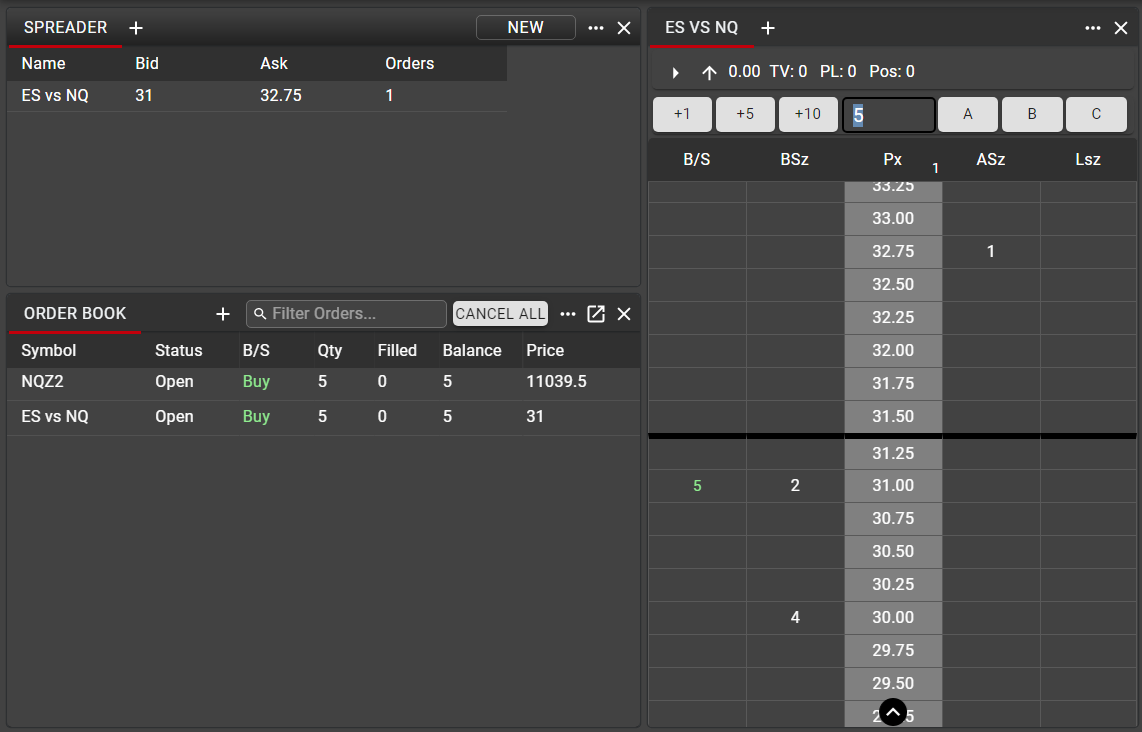
Once a synthetic spread has been displayed in a Ladder, orders may be entered and manipulated in the same manner as with any listed instruments in the Ladder. See details here on entering and managing orders from the Ladder.
The synthetic spread will also be displayed in the Order Book. Note that because only the quote leg (lead leg) is actively working orders in the market, only the parent spread order and the lead leg order are reflected in the Order Book. Not until a quote leg is filled will the hedge leg order be submitted to the market and subsequently displayed in Order Book. See next section on Spreader behavior for more details on this action.
Spreader Behavior
Spreader Configuration settings showed how to specify which leg(s) of the spread to quote and which leg(s) will be used as a hedge. The quote leg will be the instrument in which orders are actively working in the market, while the hedge leg is used as a reference point to determine where quotes should be entered in order to achieve the desired spread price.
For this reason, the hedge leg is often referred to as the driver leg, since it is the market in the hedge leg which will determine the level at which Spreader will place orders in the quote leg. This also means that the more liquid instrument is most often used as the hedge leg.
Once an order in the quote leg (or lead leg) has been executed in the market, Spreader will fire the hedge leg at the price necessary to achieve the user’s desired spread price. As specified in Spreader Configuration, this order may be entered more aggressively into the market in order to avoid hung hedge orders.
To further illustrate this behavior, it can be helpful to view the synthetic spread market in a Ladder, alongside Ladders for the individual legs.
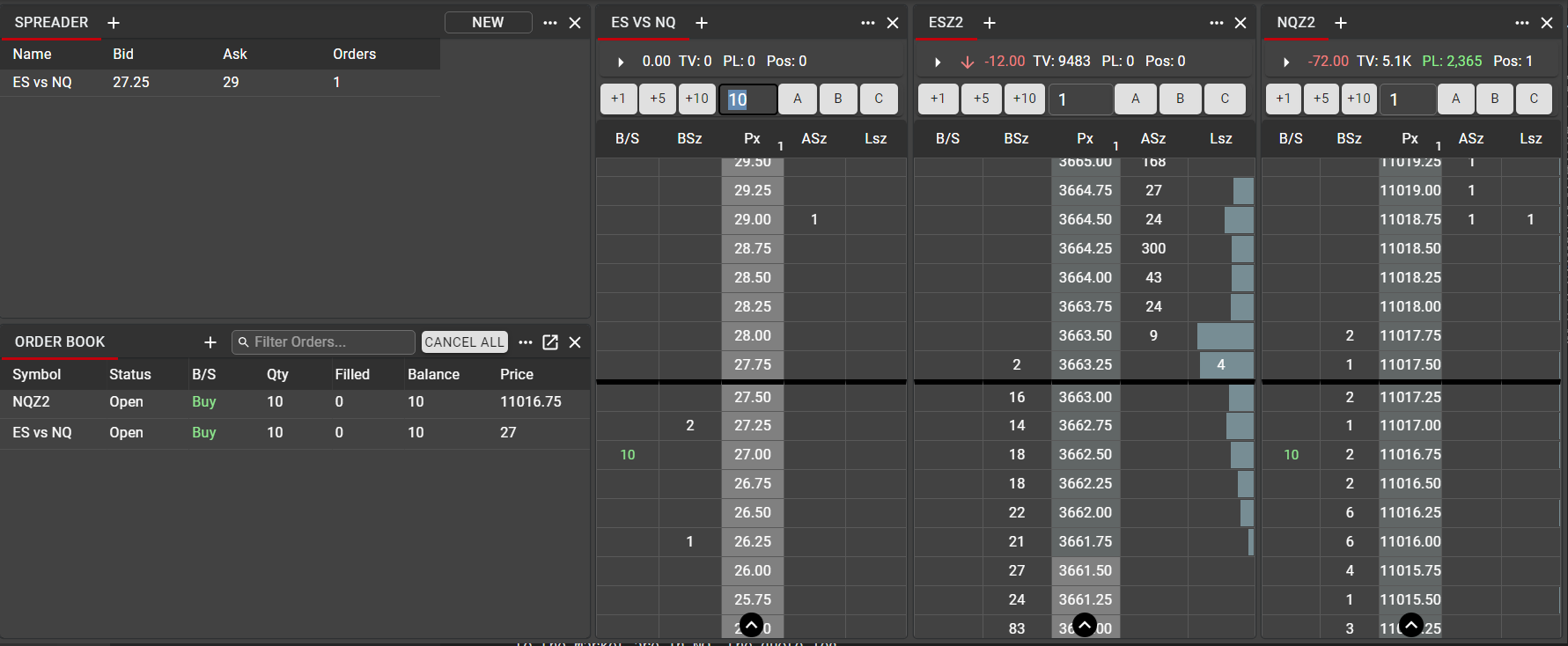
In this example, using the same ES vs NQ spread shown above, a Ladder is displayed for the generated synthetic spread market, and Ladders for each leg are displayed alongside.
Because the ES contract is more liquid than the NQ contract, ES is used as the hedge leg, or driver leg. This means that the NQ contract is the quote leg. When orders are entered in the synthetic spread, the orders sent to the market are in NQ, the quote leg.
In this example, a Buy order has been placed in the ES vs NQ spread at a price of 27.00. Spreader determines the level at which to place the quote orders which will fill this price, based on the current market in ES. Here, with the best bid in ES at 3663.25 and the Quantity Multiplier (spread ratio) set at 3:1, Spreader has placed a Buy order in NQ at a price of 11016.75.
11016.75 – 3*(3663.25) = 27.00
As the market in the hedge leg moves, Spreader will adjust the bid in the quote leg (lead leg) so that the desired spread price is maintained.
Once there is an execution in the quote leg, Spreader will fire the appropriate order in the hedge leg to achieve the desired price and quantity of the spread.
Spreader Executions
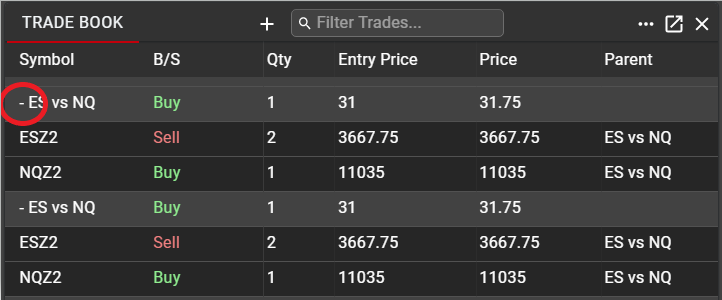
Once a synthetic spread has been executed, users may view all details in the Trade Book.
By default, only the Parent synthetic spread order will be displayed as an entry in Trade Book. The Parent spread will show the Entry Price, at which the spread order was submitted, as well as the average executed Price, based on all legs for the order.
Clicking on the expander next to the Parent spread name in the Symbol column will display all leg fills for the synthetic spread. Each leg fill will carry the Parent spread name in order to easily identify, sort and filter based on Spreader legs, as desired.
No-hedge Strategy
In the above example, a synthetic spread was created with one Quote leg and one Hedge leg. Users have the option to not hedge their spread leg if they choose, by leaving the Hedge box unchecked in the Spreader configuration.
In this configuration, the Hedge leg is being used only as a reference—or driver—price. The market in the Hedge contract still determines the price at which orders are entered in the Quote contract, but once a quote order is executed, there will be no Hedge order entered into the market. In this case, executed synthetic spreads will display in the Trade Book in the same manner as above, but the only individual leg fills will be in the Quote contract.